Multidrug Resistance Activity of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa from Urinary Tract Infected Patients in General and Private Hospitals, Amassoma
Article Sidebar
Abstract
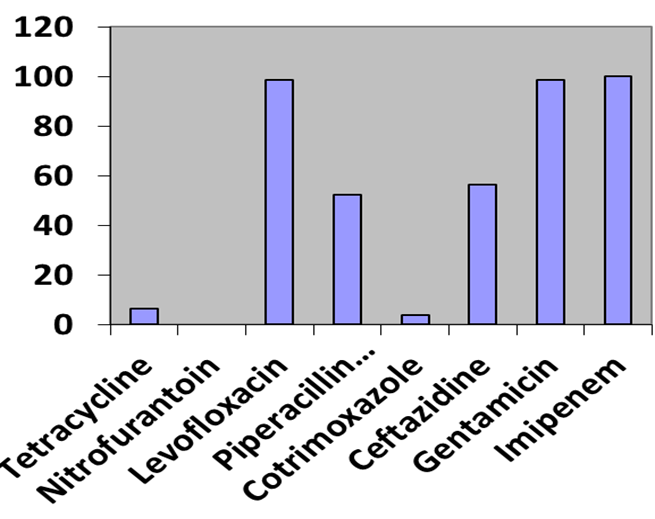
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an agent of various infections in human globally. This research was undertaken between February and June, 2021, to determine the antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to eight (8) different classes of antibiotics commonly prescribed in Nigeria hospitals. A total of 194 clinical samples which include 58 mid-stream urine, 63 wound and 73 ear samples were collected at random from General and Private (Tantua) hospitals, Amassoma community and immediately transferred to the Microbiology diagnostic laboratory, Niger Delta University for culture using Nutrient agar and Cetrimide agar. Pure isolates with 0.5 Mc Farland standard were characterised and identified using standard microbiology techniques. Antibiotics susceptibility was carried out with Mueller Hinton agar using Kirby buer and Agar diffusion method. Eighty {80} (41.2%) Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated include; urine 20(25%), ear 24(30%) and wound 36(45%); with female having a higher prevalence of 44(55%) than the male 36(45%). All the Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated was highly susceptible to imipenem(100%), levofloxacin (98.75%), gentamicin (98.75%), ceftazidine (56.5%), piperacillin tazobactam(52.5%), tetracycline (6.25%), co-trimoxazole (3.75%) and nitrofurantoin (0%). Findings showed that overall Multidrug Resistance (MDR) expressed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa was 98%, among which was 48.8% with Sulphamethoxazole trimethoprim, Tetracycline and Nitrofurantoin; more isolates were found in wound (45%), followed by ear (30%) and least in urine (25%) samples. In conclusion, imipenem (100%) was the most potent drug against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection followed by gentamicin (98.75%) and levofloxacin (98.75%); these drugs are recommended for clinical use.
Full text article
Authors
Article Details
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Oluwayemisi A. Olorode , Benson Azibanamughon Godswill , Efficacy of Nigerian Local Honey on Pseudomonas Aeruginosa from Infected Wound among Genders in Federal Medical Center, Bayelsa , Jour Med Resh and Health Sci: Vol. 6 No. 8 (2023): Journal of Medical Research and Health Sciences